What are Probiotics?
The World Health Organization defines probiotics as:
“Live microorganisms which, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit to the host”
By this definition, there are 3 key components to probiotics:
1. They must be alive
2. They have to be dosed in adequate amounts
3. And they must be bacteria of the type that confer a health benefit
Live Probiotics
Good probiotics are often pricey. They may cost extra but you can be assured that you are getting living and viable probiotics whereas some less expensive products may only contain dead bacteria. A trick to watch out for: probiotic labels that say “x billion viable/live bacteria at time of manufacture.” What the product contained at time of manufacture is completely irrelevant. It’s what they contain when you consume them that matters. What this “guarantee” is really saying is “we’re not sure how much will survive until you take them.” The better manufacturers will usually test their products for at least 6 months beyond the expiry date to ensure that you are still getting living bacteria in the amount claimed on the label when you take it. What the label should say is “guaranteed to contain x billion live or viable bacteria at time of expiry”. See the difference? Knowing that some will die off between manufacture and the time that you take them, the good manufacturers will put extra in when they make it and test it beyond the time of expiry to ensure that even if some did die off, there is still the amount stated on the label when the bottle expires.
Number of Bacteria in Probiotics
The bacteria in probiotics are listed as CFU, which stands for “colony forming units”. It means how many bacteria are in the product that can then reproduce to form a little colony. One or two billion bacteria or CFU’s per serving just doesn’t cut it. When it comes to good bacteria the higher the amount per serving the better. I would typically recommend a product that contains 35-50 billion bacteria per capsule and a wide range of species from the ones listed below. Over 100 trillion bacteria of 500 different species live in a healthy human gut, if you want to have an impact, you need to add more than a drop in the bucket.
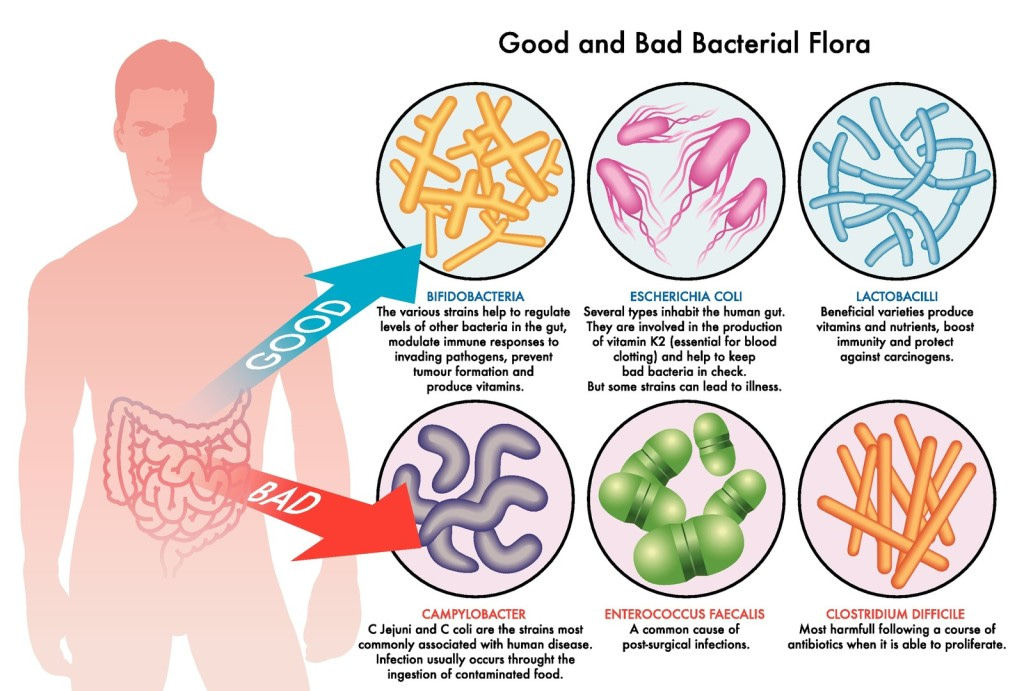
Probiotics that Give a Health Benefit
There are a few manufacturers promoting something called “soil based organisms” that are supposed to be what we naturally would have inhabiting our guts if we were eating fresh food plucked from the ground. There has been very little research supporting their use and a few case studies of people who were severely immune compromised and suffered life threatening infections after consuming these products. There is a plethora of research and human experience showing the health benefits of probiotic strains such as Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus reuteri, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium infantis, Bifidobacterium breve, Bifidobacterium longum and Bifidobacterium lactis.
What are the Health Benefits of Probiotics?
Here are the benefits of healthy good bacteria in our digestive tract:
1. Diarrhea prevention, especially when taking antibiotics
2. Colorectal cancer prevention
3. Immune system regulation and enhancement
4. Asthma and allergy prevention
5. Prevention of infection in the gut by harmful organisms like Salmonella, Shigella, H pylori, yeast etc
6. Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Irritable Bowel Syndrome
7. They provide the host with vitamins B12 and K
8. They appear to help with insulin resistance in diabetics and in women with gestational diabetes
Probiotic Foods
Certain foods are known to be rich in probiotics. These are fermented foods and many cultures have their own version. Dairy-based foods that contain probiotic bacteria include kefir and yogourt. Non-dairy probiotic foods include fermented foods like raw sauerkraut, kim chi, miso and tempeh. Do these food probiotics work? Research has been done on ingestion of bean and soy tempeh to determine their effect on gut bacteria. Soy tempeh stimulates most the growth of Bifidobacterium bacteria, while bean tempeh stimulates that of Escherichia coli. While it is good to eat probiotic-rich foods for daily gut maintenance, when taking an antibiotic, I would always encourage people to take a good quality probiotic supplement. That way we know exactly how many beneficial bacteria they are getting and of what kind. A serving of commercial yogourt may only contain 1 billion bacteria per serving where just one probiotic capsule would contain 50-100 times that much.
How Often to Take Probiotics
Whether to take probiotics and if so, how much and how often is subject to debate. Definitely any time you need to take antibiotics, you should take a good quality probiotic while taking the antibiotics and for at least two weeks afterward to prevent potentially serious side effects of taking antibiotics.
Because of the potential for numerous health benefits of taking probiotics, for most people they should be a regular part of their health maintenance program. Whether that means taking them every day, or taking them for 2-3 months out of every year, may be more to do with individual preference than scientifically proven value. I do encourage people who take probiotics daily, to try to vary the product and strains that they are taking in order to maintain the diversity of gut bacteria that seems to help promote good health.
Cautions
The above strains of probiotic bacteria are generally considered safe, even for infants. The primary contraindications for probiotic use would be:
1. Someone who is severely immune compromised such as a transplant recipient, someone very elderly or very sick, or a patient undergoing cancer treatment.
2. Using soil-based probiotics in any of the above patients and possibly in the general population as there isn’t sufficient safety and efficacy data.
With about a hundred published studies per year, there is new information being revealed every day about the health benefits of taking probiotic supplements. With almost no downside, and plenty of potential benefits, probiotics are a worthwhile addition to your health regimen.
Oh and by the way, a class action lawsuit was filed and won against Dannon/Danone in January 2008 in which the company stood accused of spending $100 million promoting clinical benefits of Activia and DanActive that its own tests had disproved. To add to that, Bifidus Regularis is a made-up name by Danone for Bifidobacterium animalis. Commercial yogurt is not an adequate means to obtain good bacteria.
Our naturopathic doctors are experts on which probiotics may work best for your particular problem as well as how to heal a whole host of gut issues. Book an appointment now.